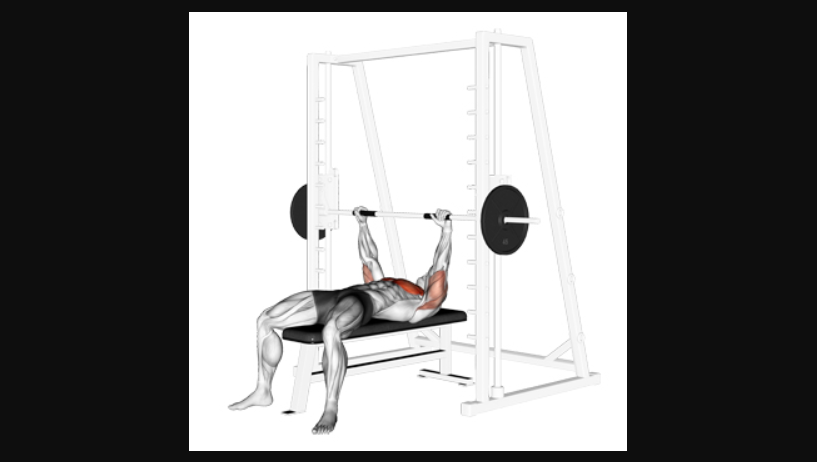
Bench press, one of the most common gym exercises for gym enthusiasts. Now it can be performed with both barbell and dumbbell. Let’s talk about the dumbbell bench press.
It targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to a well-rounded upper body workout.
This article will guide you through the process of performing the dumbbell bench press correctly, its various benefits, different variations, and essential tips to achieve maximum results.
Understanding the Dumbbell Bench Press
The dumbbell bench press is a resistance training exercise that involves lying on a flat bench while holding a dumbbell in each hand.
This exercise requires you to push the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended. Then, lower the weights in a controlled manner until they are level with your chest.
The motion resembles pushing something away from your body, engaging the chest muscles along with the shoulders and triceps.
Benefits of the Dumbbell Bench Press
The dumbbell bench press is a highly effective and versatile exercise that offers a wide range of benefits for individuals of all fitness levels. Let’s explore the advantages of incorporating the this amazing chest exercise into your workout routine in detail:
1) Comprehensive Chest Development:
The primary benefit of the bench press with dumbbells is its ability to target the pectoralis major muscles, commonly known as the chest muscles. By performing this exercise regularly, you can achieve well-rounded chest development, resulting in a more sculpted and defined chest.
By far, bench press is considered one of the best chest exercises.
2) Strengthens the Shoulders:
Along with targeting the chest muscles, the dumbbell bench press also engages the anterior deltoids, the muscles located at the front of the shoulders. Strengthening the deltoids enhances shoulder stability and functionality, reducing the risk of shoulder injuries.
3) Tricep Strengthening:
The triceps brachii, situated at the back of the upper arm, play a significant role in extending the elbows during the upward phase of the dumbbell bench press. As a result, this exercise effectively strengthens the triceps, contributing to more robust and toned arms.
4) Improved Muscle Balance:
Unlike the barbell bench press, the dumbbell bench press requires each arm to work independently. This aspect of the exercise helps correct any strength imbalances between the left and right sides of the body, promoting overall muscle balance and symmetry.
5) Enhanced Core Stability:
During the dumbbell bench press, the core muscles, including the rectus abdominis and obliques, engage to stabilize the body on the bench. This enhances core strength and stability, which are essential for overall functional fitness and injury prevention.
6) Greater Range of Motion:
Dumbbells allow a more extensive range of motion compared to barbells. You can go below chest level while doing dumbbell bench press.
As a result, the dumbbell bench presses activates a larger number of muscle fibers in the chest and shoulders, leading to better muscle development and flexibility.
This point can even make the dumbbell bench presses harder than the barbell bench presses.
7) Versatility and Variation:
The bench press with dumbbells offers various grip options, allowing you to target different areas of the chest and shoulders.
By incorporating incline, decline, and neutral grip variations, you can place emphasis on specific muscle groups for a well-rounded upper body workout.
8) Functional Strength:
As any weight exercise, dumbbell bench press also increases functional strength overtime. The chest exercise with dumbbells simulates everyday pushing movements, making it a functional exercise that translates into real-life activities.
Increased upper body strength from the dumbbell bench presses can enhance your ability to perform tasks such as pushing heavy objects or carrying groceries.
9) Enhanced Metabolism:
Compound exercises like the dumbbell bench presses require significant energy expenditure and stimulate the body’s metabolism. This can lead to increased calorie burn during and after the workout, supporting weight management and fat loss goals.
10) Accessibility:
The dumbbell bench presses can be performed in various settings, whether at the gym or in the comfort of your home with a set of dumbbells and a flat bench. Its accessibility makes it a convenient exercise for individuals with limited access to gym equipment.
Muscles Worked During the Dumbbell Bench Press
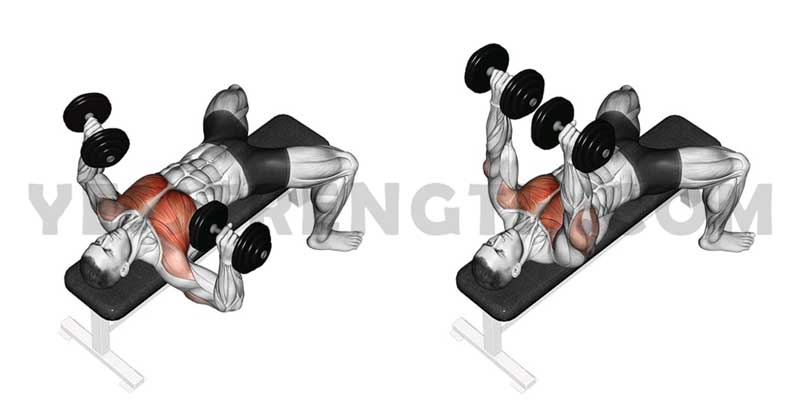
The bench press with dumbbells is a powerful compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the upper body. Let’s delve into the primary muscles involved in the dumbbell bench press:
1) Pectoralis Major (Chest Muscles):
The pectoralis major, commonly known as the chest muscles, is the primary muscle worked during the dumbbell bench presses. As you push the dumbbells away from your body, these muscles contract to generate force and move the weights upward. A well-developed pectoralis major not only enhances the appearance of the chest but also contributes to overall upper body strength.
2) Anterior Deltoids (Front Shoulder Muscles):
The anterior deltoids, located at the front of the shoulder, play a significant role in the dumbbell bench presses. They assist the chest muscles in lifting the weights and contribute to the initial push during the upward phase of the exercise. Well-developed deltoids not only improve the shoulder’s aesthetics but also enhance shoulder stability and functionality.
3) Triceps Brachii (Triceps):
The triceps brachii, situated at the back of the upper arm, are engaged during the extension phase of the dumbbell bench presses. As you push the dumbbells upwards, the triceps contract to straighten your arms fully. Strengthening the triceps is essential for various pushing movements and arm stability.
4) Biceps Brachii (Biceps):
Although the biceps are not the primary muscles worked during the dumbbell bench presses, they still play a stabilizing role in the exercise. The biceps help control the descent of the dumbbells as you lower them back to the starting position. Strong biceps are beneficial for overall arm strength and aesthetics.
5) Trapezius (Upper Back Muscles):
The trapezius muscles, located at the upper back and neck, assist in stabilizing the shoulders during the dumbbell bench presses. They help maintain proper shoulder positioning and prevent excessive strain on the shoulder joints.
6) Serratus Anterior (Side Muscles of the Chest):
The serratus anterior muscles lie between the ribs and the scapulae. They play a role in scapular protraction during the upward phase of the exercise, contributing to shoulder stability and proper movement mechanics.
7) Rectus Abdominis (Abdominal Muscles):
The rectus abdominis, commonly referred to as the abs, engage in the dumbbell bench presses to stabilize the core and maintain proper posture on the bench. A strong core is crucial for overall strength and injury prevention.
Proper Form and Technique for Dumbbell Bench Press
To perform the dumbbell bench press correctly and avoid injuries, follow these steps:
- Lie flat on a bench with your feet firmly planted on the ground.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder level with your palms facing forward.
- Lower the dumbbells slowly and under control, keeping your elbows slightly less than 90-degree angle.
- Push the dumbbells upwards in a straight line until your arms are fully extended.
- Squeeze your chest muscles at the top of the movement, then gradually lower the weights back down.
- Now repeat the process as many times as you want.
Variations of Dumbbell Bench Press
- Incline Dumbbell Bench Press: Perform the exercise on an inclined bench to target the upper chest muscles.
- Decline Dumbbell Bench Press: Perform the exercise on a decline bench to emphasize the lower chest muscles.
- Neutral Grip Dumbbell Bench Press: Hold the dumbbells with a neutral grip (palms facing each other) to reduce stress on the shoulders.
- Single Arm Dumbbell Bench Press: Alternate doing the bench press with dumbbell with each arm at a time.
Incorporating Dumbbell Bench Press in Your Workout Routine
The bench press with dumbbells can be a valuable addition to your upper body workout routine. Consider the following tips:
- Warm-up: Always warm up before lifting to prepare your muscles and prevent injuries.
- Sets and Repetitions: Aim for 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions to build both strength and muscle mass.
- Rest: Allow 1-2 minutes of rest between sets to recover adequately as a beginner.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the exercise.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Arching Your Back too much: Keep your back flat or little arched on the bench to prevent straining your lower back.
- Bouncing the Weights: Avoid using momentum to lift the dumbbells; focus on controlled movements.
- Neglecting Full Range of Motion: Lower the weights until your elbows are at 90 degrees for optimal results.
Tips for Maximizing Results
- Mind-Muscle Connection: Focus on engaging your chest muscles throughout the movement.
- Breathing: Exhale as you push the weights up and inhale as you lower them down.
- Proper Grip: Hold the dumbbells firmly to maintain stability during the exercise.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the exercise.
Precautions and Safety Measures
- Consult a Professional: If you are new to strength training, seek guidance from a fitness trainer.
- Start Light: Begin with lighter weights to master the form before increasing the load.
- Avoid Overtraining: Allow your muscles time to recover between workouts.
Conclusion
The dumbbell bench press is a versatile and effective exercise that can significantly contribute to your upper body strength and muscle development. It has many benefits that can help you grow and strengthen your chest muscles and can also help in maintaining muscle balance on both sides.
By understanding the proper form, various variations, and essential tips, you can make the most out of this exercise.
As always, remember to prioritize safety, maintain a consistent workout routine, and enjoy the benefits of a well-toned and strong upper body.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Is the dumbbell bench press suitable for beginners?
Yes, the dumbbell bench press is suitable for beginners. Start with lighter weights and focus on proper form.
2) Can I do the dumbbell bench press with shoulder pain?
If you experience shoulder pain, it is better to stop doing the exercise and seek medical guidance first.
3) Can women benefit from the dumbbell bench press?
Absolutely! The dumbbell bench press is beneficial for both men and women looking to strengthen their upper body.
4) How often should I do the dumbbell bench press?
You can include the dumbbell bench presses in your workout routine 1-2 times a week, with proper rest between sessions.
5) What if I don’t have access to a bench?
In the absence of a bench, you can perform the exercise on the floor or a stable surface.