Already know about the flat bench press and want to perfect the form? Or looking for an exercise that is excellent for chest and chest day, well flat bench press is among the best chest exercises. It is also one of the most common gym exercises for the chest.
The flat bench press is one of the most effective exercises to develop and strengthen your chest, shoulders, and triceps. You can definitely include it in your push day workout routine. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced lifter, mastering the proper form and technique is crucial for maximizing your results and minimizing the risk of injury.
In this article, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to perform the flat bench press correctly. Let’s dive in!
Introduction
The flat bench press is a compound exercise that primarily targets the pectoral muscles, but also engages the triceps and deltoids.
It is a staple exercise in strength training and bodybuilding routines due to its ability to stimulate muscle growth and increase upper body strength.
Whether your goal is to gain muscle mass or improve your overall fitness, the flat bench press is an exercise you should incorporate into your workout routine.
Benefits of Flat Bench Press
The flat bench press offers numerous benefits beyond building an impressive chest. Here are some key advantages:
1) Muscle Development and Strength
Performing the flat chest press regularly can lead to significant muscle gains in your chest, shoulders, and triceps. It is a compound movement that activates multiple muscle groups, promoting overall upper body strength and stability.
2) Functional Fitness
The strength gained from flat bench press transfers to everyday activities and sports. It helps with pushing movements, such as opening doors or pushing objects, and improves athletic performance in sports like basketball, football, and tennis.
3) Increased Bone Density
Weight-bearing exercises like the flat chest press stimulate bone growth and increase bone density. This can be especially beneficial for individuals at risk of osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions.
4) Metabolic Boost
The flat bench press, being a compound exercise, recruits a large number of muscles. This results in a higher calorie burn during and after the workout, helping to increase your overall metabolic rate.
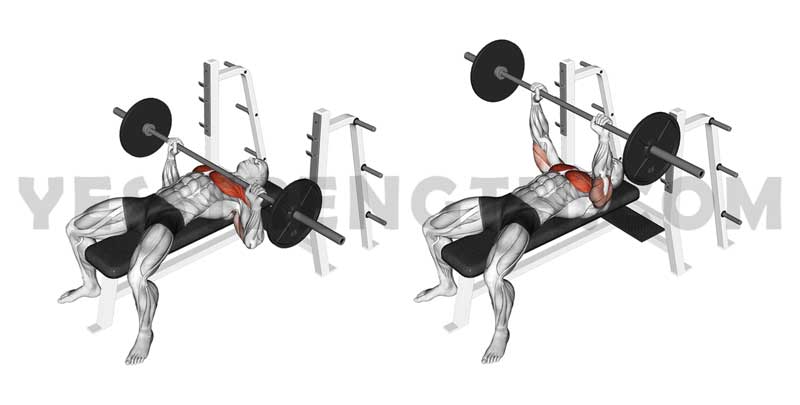
Flat Bench Press: Muscles Worked
The flat bench press is an excellent compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups in the upper body. Understanding the primary and secondary muscles worked during this exercise can help you better target and develop specific areas. Here are the key muscles targeted:
1) Pectoralis Major (Chest Muscles)
The pectoralis major is the primary muscle group targeted during the flat chest press. It consists of two heads, the clavicular head (upper chest) and the sternal head (lower chest). The flat chest press helps develop both heads, contributing to a well-rounded chest.
2) Anterior Deltoids (Front Shoulders)
The anterior deltoids, located at the front of the shoulder, are heavily involved in the flat chest press. They assist in stabilizing the shoulders and contribute to the pressing motion.
3) Triceps Brachii (Triceps)
The triceps brachii, located at the back of the upper arm, act as synergists during the flat chest press. They assist the chest muscles in extending the elbows and completing the pressing movement.
4) Serratus Anterior
The serratus anterior, also known as the “boxer’s muscle,” is located on the sides of the ribcage. It is engaged during the flat chest press to stabilize the shoulder blades and maintain proper form.
5) Trapezius (Upper Back)
The trapezius muscle, located in the upper back and neck area, is engaged during the flat chest press to stabilize and support the shoulders and spine.
6) Rhomboids (Upper Back)
The rhomboids, located between the shoulder blades, assist in scapular retraction and help maintain proper posture and stability during the exercise.
7) Biceps Brachii (Biceps)
Although not the primary muscle group worked during the flat chest press, the biceps brachii act as stabilizers and assist in maintaining grip on the barbell.
It’s important to note that while the flat chest press primarily targets the muscles mentioned above, it also engages other smaller stabilizer muscles in the shoulders, arms, and upper back to provide stability and support throughout the movement.
Equipment Needed
Before starting the flat bench press, you will need the following equipment:
- A flat bench: Make sure it is sturdy and properly adjusted to a comfortable height.
- A barbell or a dumbbell: Choose an appropriate weight based on your strength and fitness level.
- Weight plates: Add weight plates to the barbell as per your desired resistance.
- Collars: Use collars to secure the weight plates in place and ensure safety.
Proper Setup and Technique
To perform the flat bench press with proper form, follow these steps:
- Lie down: Position yourself on the flat bench with your back flat against it. Keep your feet firmly planted on the floor.
- Grip the bar: Grasp the barbell with a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Your palms should face forward.
- Unrack the bar: Lift the barbell off the rack, holding it directly above your chest with your arms fully extended.
- Lower the bar: In a controlled manner, lower the barbell to your mid-chest while keeping your elbows slightly tucked in. Maintain tension in your chest and engage your core.
- Press the bar: Push the barbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms while exhaling. Focus on squeezing your chest muscles at the top of the movement.
- Repeat: Complete the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When performing the flat bench press, it’s important to avoid these common mistakes:
- Arching your back excessively: Maintain a natural arch in your lower back, but avoid excessive arching, as it can lead to lower back injuries.
- Bouncing the bar off your chest: Control the descent of the bar and avoid bouncing it off your chest. This ensures that your muscles are engaged throughout the entire range of motion.
- Lifting your feet off the ground: Keep your feet planted firmly on the floor to maintain stability and generate power from the ground up.
- Using improper grip width: Choose a grip width that allows for optimal engagement of your chest muscles. A grip that is too wide or too narrow may put unnecessary strain on your shoulders and wrists.
- Neglecting proper warm-up: Always warm up before performing heavy bench presses to prepare your muscles and joints for the exercise.
Variations and Alternatives
While the flat bench press is a fundamental exercise, incorporating variations and alternatives can add variety to your training routine and target specific muscle groups. Here are some options:
- Incline Bench Press: Targets the upper chest and shoulders.
- Decline Bench Press: Focuses on the lower chest and triceps.
- Dumbbell Bench Press: Enhances stability and allows for a greater range of motion.
- Push-Ups: A bodyweight alternative that engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
Training Tips and Safety Precautions
To optimize your flat bench press and ensure safety, consider the following tips:
- Start with a warm-up: Perform dynamic stretches and lightweight sets to warm up your muscles and increase blood flow.
- Gradually increase the weight: Progressively increase the weight you lift as your strength improves, but always prioritize proper form.
- Use a spotter: When lifting heavy weights, have a spotter available to assist you if needed and provide an extra layer of safety.
- Listen to your body: If you experience pain or discomfort, adjust your form or seek guidance from a fitness professional to prevent injuries.
- Allow for adequate rest: Rest days are crucial for muscle recovery and growth. Avoid overtraining and prioritize rest and sleep.
Sample Workout Routine
Here’s a sample workout routine incorporating the flat bench press:
| Exercise | Sets | Repetitions |
| Flat Bench Press | 3 | 8-10 |
| Incline Dumbbell Press | 3 | 10-12 |
| Bent-Over Rows | 3 | 8-10 |
| Overhead Press | 3 | 10-12 |
| Tricep Dips | 3 | 12-15 |
Remember to adjust the weight and repetitions based on your fitness level and goals. This sample workout routine incorporates the flat chest press as the primary exercise and includes additional exercises to target other muscle groups in the upper body. It provides a balanced approach to strength and muscle development.
Nutrition and Recovery
To support your strength training and optimize your results, focus on a balanced diet that includes:
- Adequate protein intake for muscle repair and growth.
- Complex carbohydrates for energy.
- Healthy fats for hormone production and joint health.
- Sufficient hydration for optimal performance.
Additionally, prioritize post-workout recovery by incorporating stretching, foam rolling, and quality sleep into your routine.
Conclusion
The flat bench press is a highly effective exercise for developing upper body strength and muscle mass. By mastering the proper technique and incorporating it into your training routine, you can achieve impressive results.
Remember to focus on proper form, gradually increase the weight, and listen to your body to prevent injuries. Combine the flat chest press with a well-rounded workout routine, proper nutrition, and adequate rest to optimize your progress and achieve your fitness goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1) Is the flat bench press suitable for beginners?
Yes, the flat bench press can be performed by beginners; however, it’s important to start with lighter weights and focus on proper form.
2) How often should I perform the flat bench press?
The frequency depends on your training program and goals. As a general guideline, 2-3 times per week with a day of rest in between sessions is recommended.
3) Can I do the flat bench press with dumbbells?
Yes, the dumbbell bench press is a great alternative to the barbell bench press and offers added benefits of stability and increased range of motion.
4) Can women benefit from the flat bench press?
Absolutely! Women can benefit from the flat bench press as it helps to strengthen and shape the chest muscles.
5) Should I warm up before performing the flat bench press?
Yes, warming up is essential to prepare your muscles and joints for the exercise. Perform dynamic stretches and lightweight sets before starting your working sets.
6) Can the flat bench press help improve posture?
Yes, the flat bench press strengthens the muscles responsible for good posture, such as the upper back and shoulders.
7) Is it necessary to touch the barbell to your chest during the flat bench press?
While it is important to lower the barbell to your chest, it’s not necessary to touch it. Lower the bar until your elbows are at a 90-degree angle for optimal muscle engagement.
8) Are there any alternatives for people with shoulder injuries?
If you have shoulder injuries, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified fitness trainer for exercises that are suitable for your specific condition.
9) Can I do the flat bench press without a spotter?
While having a spotter adds an extra layer of safety, you can still perform the flat bench press without one by using safety bars or a Smith machine, which provide built-in safety mechanisms.





